


Gastroenterology is the study of the normal function and diseases of the...
What is Hepatology?
Hepatology is a specialized branch of medicine focused...

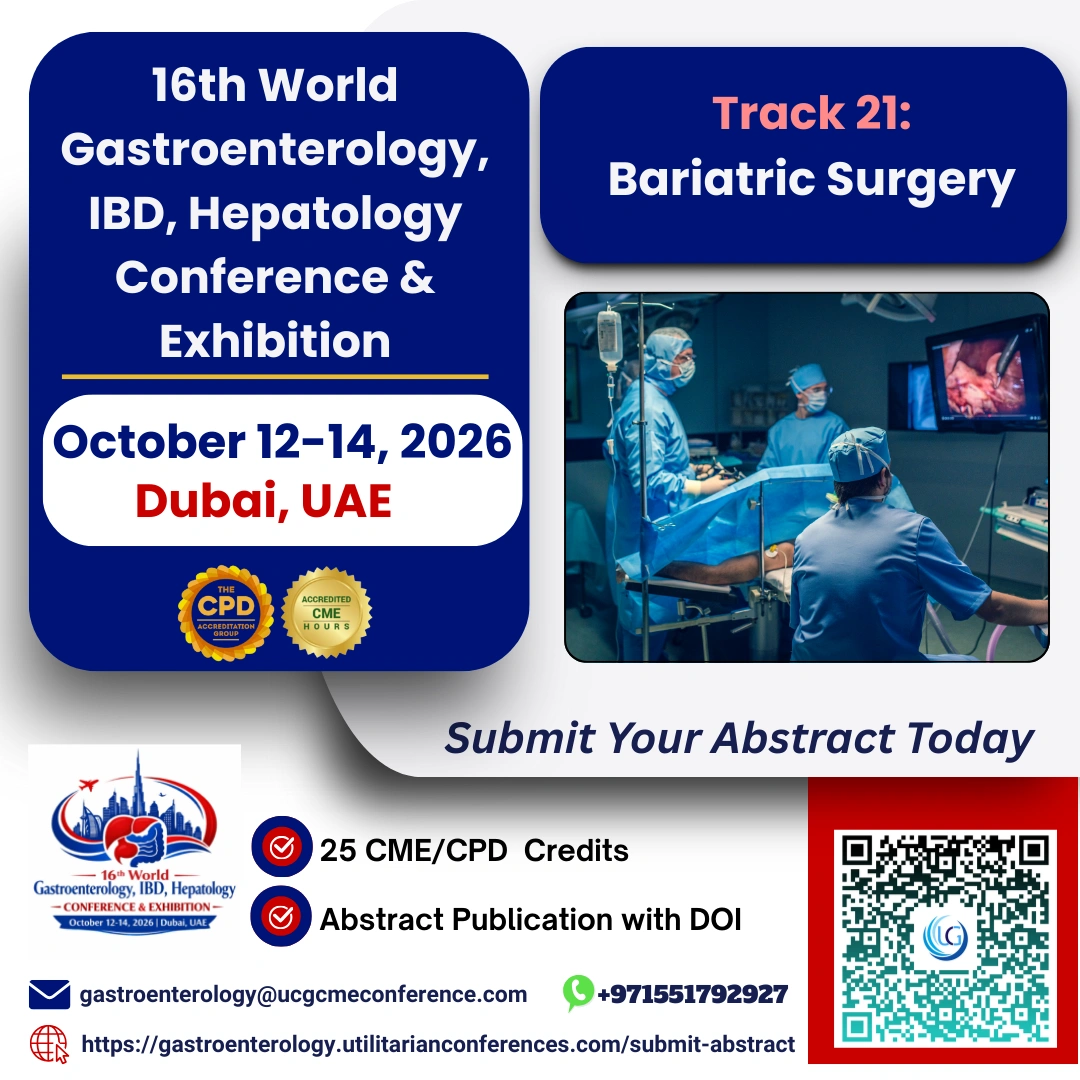
Bariatric surgery is a type of surgical procedure performed
on individuals who are severely obese, often as a last resort when other weight
loss methods have failed to yield significant results. The primary goal of
bariatric surgery is to promote weight loss and improve overall health by
altering the digestive system's anatomy and physiology, which leads to reduced
food intake, decreased absorption of nutrients, or both.
There are several types of bariatric surgery, including:
1. Gastric Bypass: In gastric bypass surgery, the surgeon
creates a small pouch at the top of the stomach and connects it directly to the
small intestine, bypassing a portion of the stomach and the first section of
the small intestine (duodenum). This reduces the amount of food the stomach can
hold and alters the absorption of nutrients.
2. Sleeve Gastrectomy: This procedure involves removing a
large portion of the stomach, leaving behind a smaller, banana-shaped
"sleeve" or tube-shaped stomach. The reduced stomach size limits the
amount of food that can be consumed, leading to weight loss.
3. Adjustable Gastric Band: A silicone band is placed around
the upper part of the stomach, creating a small pouch above the band and a
narrow passage to the rest of the stomach. The band can be adjusted by adding
or removing saline solution, which affects the size of the opening between the
two parts of the stomach.
4. Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch (BPD/DS):
This procedure involves removing a large portion of the stomach and rerouting
the intestines to reduce the absorption of calories and nutrients.
Bariatric surgery is not a cosmetic procedure; it is
intended for individuals with severe obesity or those with obesity-related
health conditions such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, or sleep apnea.
The surgery can lead to significant weight loss, improvement in obesity-related
health conditions, and enhanced quality of life.
However, bariatric surgery is not without risks and
potential complications. Patients must undergo a thorough evaluation by a
healthcare team, including a surgeon, nutritionist, psychologist, and other
specialists, to determine if they are suitable candidates for surgery and to
ensure they understand the risks and benefits involved.
Post-surgery, patients must adhere to strict dietary and
lifestyle changes, including adopting a healthy eating plan and engaging in
regular physical activity, to achieve and maintain successful weight loss
outcomes and minimize complications. Regular follow-up appointments and ongoing
support from healthcare providers are essential for long-term success after bariatric
surgery.
Bariatric Surgery profession
The field of bariatric surgery involves several professions
that work collaboratively to provide comprehensive care to patients undergoing
weight loss surgery. Here are the key professions involved:
Bariatric Surgeon: Bariatric surgeons are medical doctors who specialize in performing weight loss surgeries. They have advanced training and expertise in various bariatric procedures, including gastric bypass, sleeve gastrectomy, gastric banding, and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Bariatric surgeons assess patients' eligibility for surgery, perform the procedures, and provide post-operative care.
Bariatric Nurse: Bariatric
nurses are registered nurses (RNs) or advanced practice nurses (such as nurse
practitioners or clinical nurse specialists) who specialize in caring for
patients undergoing bariatric surgery. They assist with pre-operative
education, provide emotional support to patients and their families, monitor
patients' health status during and after surgery, and educate patients about
post-operative care and lifestyle changes.
Registered Dietitian/Nutritionist: Registered dietitians
(RDs) or nutritionists specializing in bariatric care play a crucial role in
helping patients achieve successful weight loss and maintain optimal nutrition
before and after surgery. They develop individualized nutrition plans, provide
dietary education, monitor patients' nutritional status, and support patients
in making healthy food choices to support weight loss and overall health.
Psychologist/Psychiatrist: Mental health professionals,
including psychologists and psychiatrists, are often part of the bariatric
surgery team to assess patients' psychological readiness for surgery, provide
counseling and support, and address any emotional or behavioral factors that
may impact patients' ability to adhere to post-operative lifestyle changes.
Exercise Physiologist/Physical Therapist: Exercise
physiologists or physical therapists may work with bariatric surgery patients
to develop personalized exercise programs tailored to their needs and
abilities. Regular physical activity is an essential component of weight
management and overall health following bariatric surgery.
Endocrinologist/Diabetologist: Endocrinologists or
diabetologists specialize in the management of hormonal and metabolic
disorders, including obesity and type 2 diabetes. They may be involved in
evaluating patients' metabolic health before and after surgery and managing
diabetes medications or other hormonal therapies as needed.
Anesthesiologist: Anesthesiologists are physicians who
specialize in administering anesthesia and managing patients' pain during
surgery. They play a critical role in ensuring patients' safety and comfort
during bariatric procedures.
These professions work together as part of a multidisciplinary team to provide comprehensive care to patients undergoing bariatric surgery, addressing various aspects of physical, emotional, and nutritional well-being before, during, and after the surgical procedure.
Sub Track: Norovirus, Viral Infections, Rotavirus, Adenovirus, Astrovirus, Bacterial Infections, Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Shigella, Clostridium difficile, Parasitic Infections, Giardia lamblia, Cryptosporidium, Entamoeba histolytica, Diarrhea, Vomiting, Abdominal Pain and Cramps, Fever, Nausea, Diagnosis, Clinical Assessment, Rehydration, Antibiotics, Antiparasitic Medications, Probiotics, Symptomatic Treatment