


Gastroenterology is the study of the normal function and diseases of the...
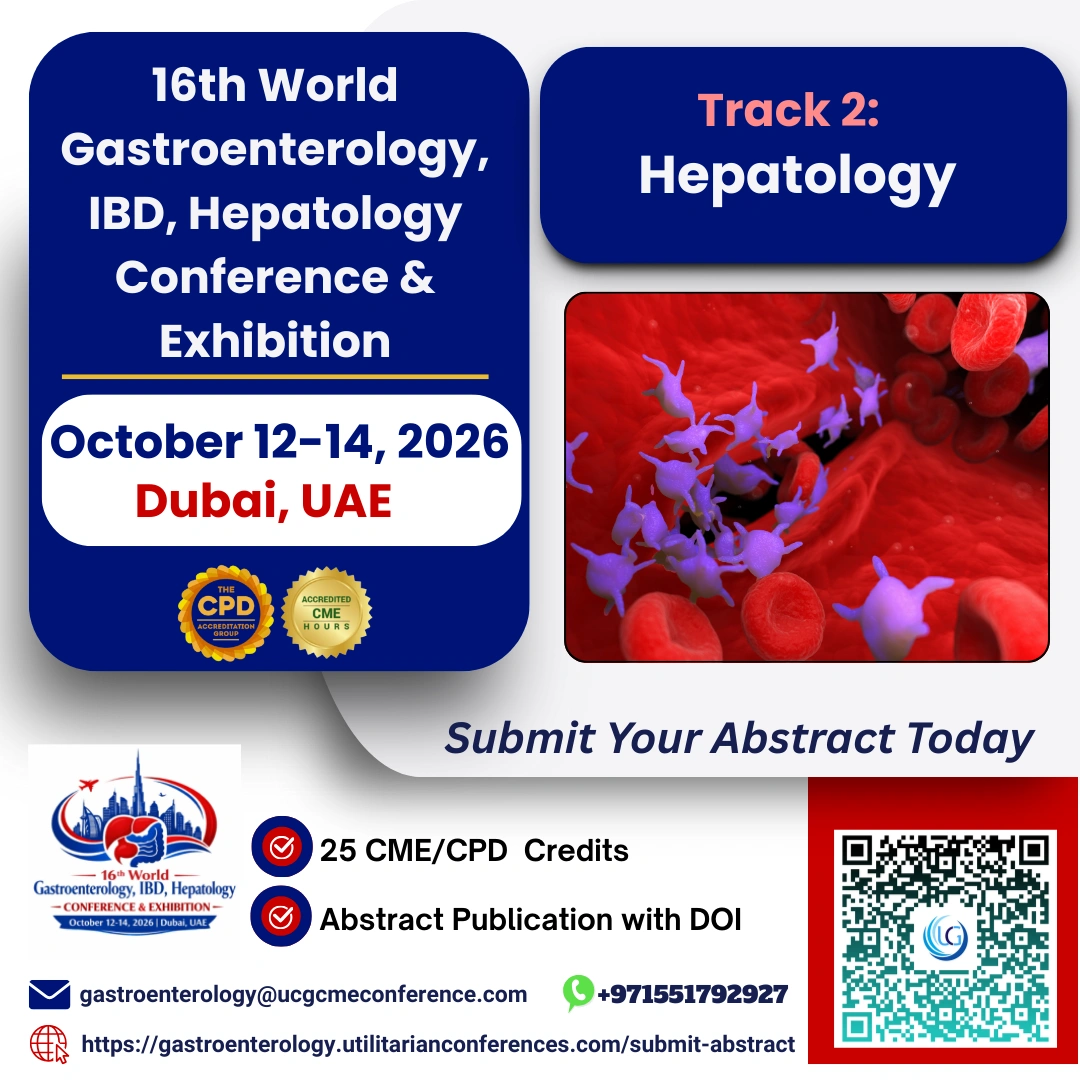
What is Hepatology?
Hepatology is a specialized branch of medicine focused...

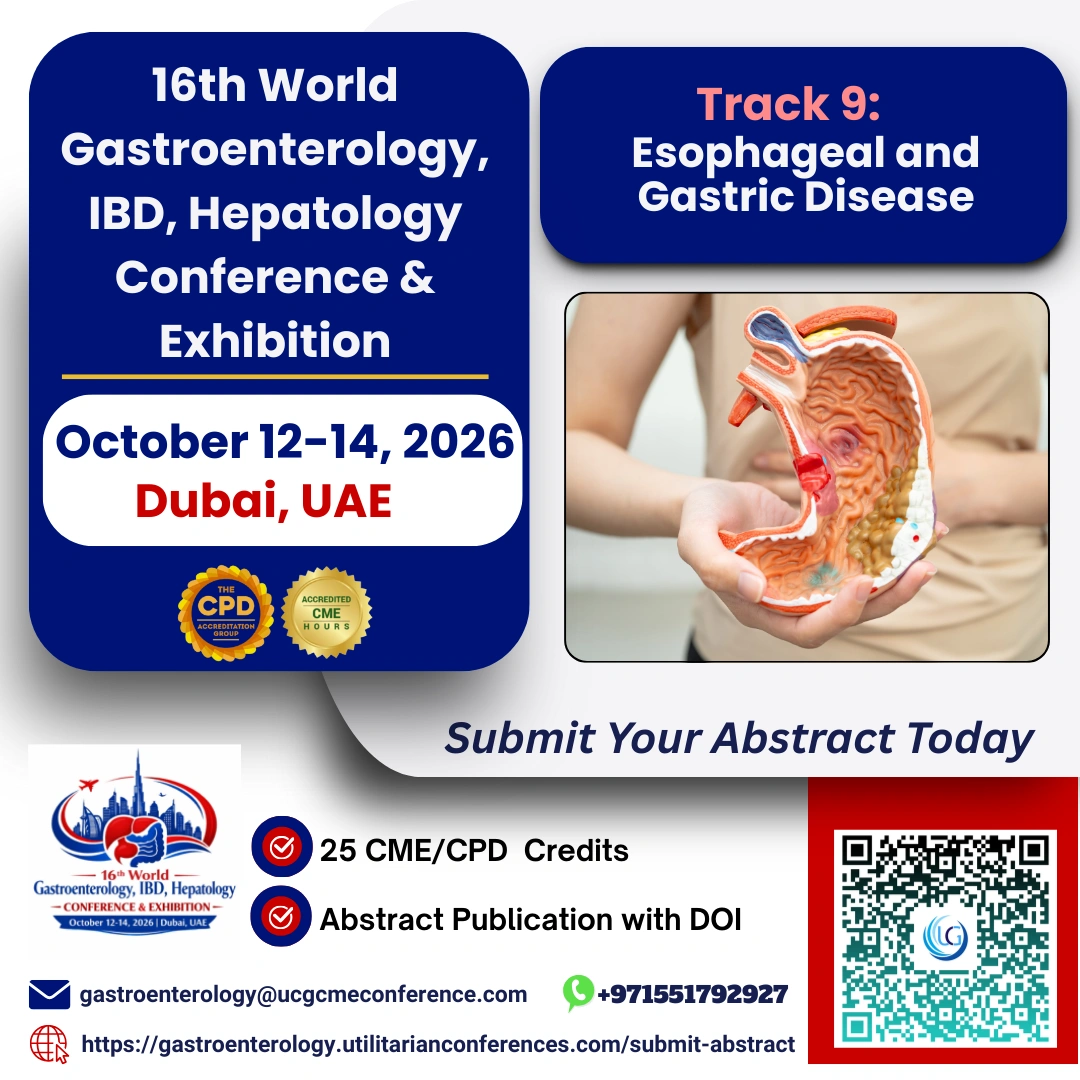
Esophageal and gastric diseases encompass a range of conditions affecting the digestive system. These ailments can significantly impact one's quality of life and require attention and care for effective management. In this blog, we delve into the complexities of esophageal and gastric diseases, exploring their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
1. Understanding Esophageal and Gastric Diseases:
The esophagus and stomach play vital roles in the digestive process. The esophagus is a muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) with the stomach, allowing food and liquids to pass through. The stomach, on the other hand, is a muscular organ that further breaks down food through the secretion of acids and enzymes.
2. Various factors can lead to the development of esophageal and gastric diseases, including:
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): This common condition occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. Chronic GERD can lead to complications such as esophagitis, esophageal strictures, and Barrett's esophagus—a condition that increases the risk of esophageal cancer.
Peptic Ulcers: Peptic ulcers are sores that develop on the lining of the stomach, esophagus, or small intestine. They are often caused by infection with Helicobacter pylori bacteria, prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), or excessive alcohol consumption.
3. Esophageal Cancer: Esophageal cancer is a serious and often aggressive disease that develops in the tissues of the esophagus. It is associated with risk factors such as smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, obesity, and chronic GERD.
Symptoms and Diagnosis:
The symptoms of esophageal and gastric diseases can vary depending on the specific condition but may include:
1. Heartburn
2. Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia)
3. Chest pain or discomfort
4. Nausea and vomiting
5. Abdominal pain
6. Unintentional weight loss
Diagnosis often involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests such as endoscopy, barium swallow, esophageal pH monitoring, and blood tests.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for esophageal and gastric diseases depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Common treatment options include:
Lifestyle Modifications: Dietary changes, weight management, smoking cessation, and avoiding triggers such as spicy foods and alcohol can help alleviate symptoms of GERD and other digestive disorders.
Medications: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), H2-receptor antagonists, antacids, antibiotics (for H. pylori infection), and prokinetic agents may be prescribed to reduce acid production, relieve symptoms, and promote healing of ulcers.
Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments fail or complications arise, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical procedures for esophageal and gastric diseases include fundoplication (to treat GERD), endoscopic mucosal resection (for early-stage cancers), and gastrectomy (partial or total removal of the stomach).
Conclusion:
Esophageal and gastric diseases can significantly impact one's health and well-being. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and improved outcomes. If you experience persistent symptoms related to digestion or suspect you may have an esophageal or gastric condition, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and personalized treatment recommendations. With prompt diagnosis and appropriate care, many individuals can effectively manage these conditions and lead fulfilling lives.
Sub Track: Esophageal Diseases, Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease, Esophageal Dilation, Esophageal Stricture, Barrett's Esophagus, Esophageal Cancer, Gastritis, Gastric (Stomach) Diseases, Peptic Ulcer Disease, Gastric Cancer, Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor, General Considerations,