


Gastroenterology is the study of the normal function and diseases of the...
What is Hepatology?
Hepatology is a specialized branch of medicine focused...

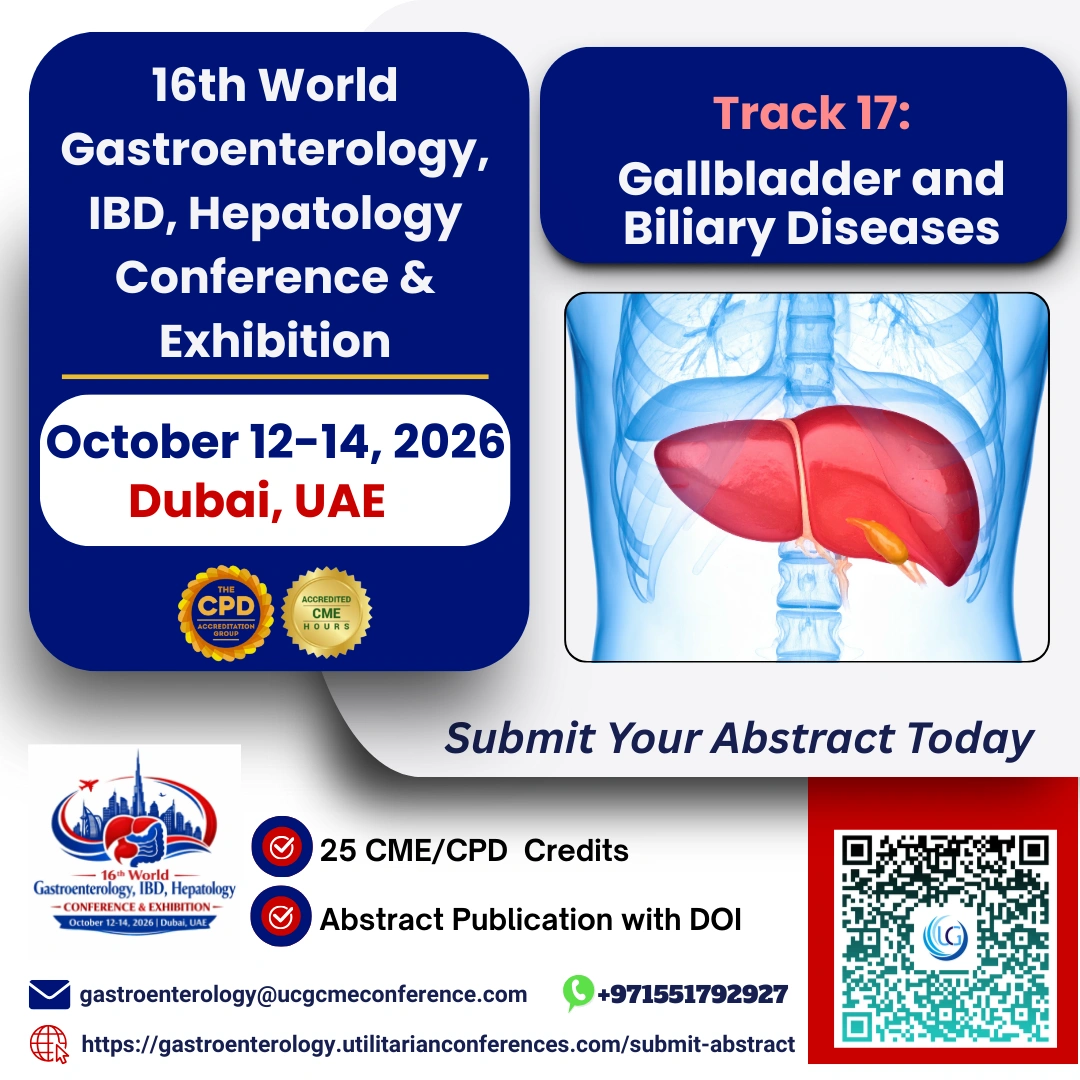
The gallbladder and biliary system
play essential roles in the digestion and metabolism of fats, serving as
integral components of the digestive process. However, when dysfunction or
disease affects these vital structures, it can lead to significant discomfort,
complications, and impaired quality of life. In this blog, we delve into the
intricacies of gallbladder and biliary diseases, exploring their causes,
symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive strategies.
Understanding Gallbladder and Biliary Diseases
Gallbladder and biliary diseases
encompass a range of conditions affecting the gallbladder, bile ducts, and
associated structures. Common disorders include:
1.
Gallstones (Cholelithiasis): Hardened deposits
of cholesterol or bilirubin that form in the gallbladder or bile ducts.
2.
Cholecystitis: Inflammation of the gallbladder,
often triggered by gallstone obstruction.
3.
Biliary Colic: Intense, episodic abdominal pain
resulting from gallstone obstruction of the bile ducts.
4.
Choledocholithiasis: Presence of gallstones in
the common bile duct.
5.
Biliary Dyskinesia: Impaired gallbladder
motility leading to symptoms of biliary colic without evidence of gallstones.
6.
Cholangitis: Infection and inflammation of the
bile ducts, typically secondary to bile duct obstruction.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Gallbladder and biliary diseases present with a variety of symptoms,
including:
I.
Abdominal pain: Typically located in the upper
right quadrant or epigastric region and may radiate to the back or shoulder.
II.
Nausea and vomiting: Especially after consuming
fatty meals.
III.
Fever and chills: Signs of infection in cases of
acute cholecystitis or cholangitis.
IV.
Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes due to
bile duct obstruction.
Diagnosis of gallbladder and biliary
diseases involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies
(ultrasound, CT scan, MRI), blood tests (liver function tests, bilirubin
levels), and occasionally, endoscopic procedures (ERCP) for visualization and
intervention.
Treatment Options
Treatment for gallbladder and
biliary diseases depends on the specific condition and its severity. Common
interventions include:
I.
Lifestyle modifications: Dietary changes, weight
management, and avoidance of fatty foods to minimize symptoms.
II.
Medications: Pain management, antibiotics for
infections, and bile acid medications to dissolve gallstones (ursodeoxycholic
acid).
III.
Endoscopic procedures: ERCP with sphincterotomy
and stone extraction for choledocholithiasis or biliary strictures.
Surgical interventions:
Laparoscopic cholecystectomy for symptomatic gallstones or cholecystitis, and
bile duct surgery for complex biliary diseases.
Preventive Strategies
While some risk factors for
gallbladder and biliary diseases, such as genetics and age, cannot be modified,
adopting healthy lifestyle habits can help reduce the risk and severity of
these conditions. Key preventive strategies include:
I.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Obesity is a
significant risk factor for gallstones and gallbladder disease.
II.
Eating a balanced diet: Emphasizing fruits,
vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting saturated fats and
cholesterol-rich foods.
III.
Staying hydrated: Drinking an adequate amount of
water helps prevent gallstone formation.
IV.
Avoiding rapid weight loss: Gradual weight loss
is preferred to prevent gallstone formation due to rapid changes in bile
composition.
Conclusion
Gallbladder and biliary diseases
pose significant challenges to individuals' health and well-being,
necessitating timely diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and preventive measures.
By raising awareness, promoting healthy lifestyle habits, and fostering
collaboration between patients and healthcare providers, we can navigate the
terrain of gallbladder and biliary diseases with greater resilience and optimism.
Through continued research, innovation, and patient education, we can strive to alleviate suffering, improve outcomes, and promote optimal digestive health for individuals affected by these conditions. Together, let us embrace a holistic approach to care and empower individuals to take proactive steps toward gallbladder and biliary health, ensuring a brighter, healthier future for all.